Export mode is one of the most important data export options. It specifies the main export action. In the description of every export format, you can find all export modes which belong to it. In this topic, all export modes are collected, with some additional details.
The data export modes can work differently depending on export format. The most significant differences are between exporting to file formats and exporting to databases.
Export Modes for Exporting to File Formats
REPLACE+INSERT
The target file is created and filled with incoming rows; if the target file already exists, it is overwritten. Overwrite prompt is displayed if the corresponding setting is in place, except when exporting from command line in silent mode.
CREATE_OR_REPLACE
A blank target file (using appropriate structure) is created; if the target file already exists, it is overwritten. Overwrite prompt is displayed if the corresponding setting is in place, except when exporting from command line in silent mode.
For most formats, it will produce the blank file with column headers (if any). But for some formats, it could be more complex result; for example, for Text/CSV, if the Schema option is not Standard, a separate schema will also be created.
APPEND
The target file is appended with incoming rows; if the target file does not exist, it is created. Available only in Exportizer Pro and Exportizer Enterprise.
This mode is supported for several formats only:
| Text/CSV | The schema, field structure and most of the export options like Encoding must be compatible with existing target. |
| JSON | The field structure and most of the export options must be compatible with existing target. |
| HTML | The field structure and most of the export options must be compatible with existing target. But for some cases, more complex rules are applied; read the format description for details. |
| XML | The field structure must be compatible with existing target. |
| SQL Script | The field structure and most of the export options must be compatible with existing target. |
Export Modes for Exporting to Databases
Exporting to databases is available only in Exportizer Enterprise and Exportizer Pro; the latter one can export only to ODBC data sources. Use Database export format for that.
REPLACE+INSERT
The target table is created and filled with incoming rows; if the target table already exists, it is overwritten. Overwrite prompt is displayed if the corresponding setting is in place, except when exporting from command line in silent mode.
CREATE_OR_REPLACE
A blank target table (using appropriate structure) is created; if the target table already exists, it is overwritten. Overwrite prompt is displayed if the corresponding setting is in place, except when exporting from command line in silent mode.
APPEND
The target table is appended with incoming rows; if the target table does not exist, it is created.
The field structure of the source must be compatible with existing target structure.
EMPTY+INSERT
The target table is emptied before inserting incoming rows; if the target table does not exist, it is created. Data delete prompt is displayed if the corresponding setting is in place, except when exporting from command line in silent mode.
The field structure of the source must be compatible with existing target structure.
UPDATE
The records in the target table that match incoming records, are updated with incoming records. Key fields must be defined to match the records.
Notes
- The target must already exist and should have an index defined to match the records.
- The types and sizes of the source fields chosen for the updating must be compatible with existing target fields. You can choose which fields to update, in Field Mappings section
- Use this mode carefully when the key fields (either source or target) can contain NULL values.
- Use this mode carefully for multi-table exporting.
- This mode may work differently for different target database types/interfaces, therefore it is recommended to test it carefully before using on production systems. Consider to use different combinations of Memory saving mode and Use SQL parameters options to find the best results.
APPEND+UPDATE
The records in the target table that match incoming records, are replaced with incoming records. Unmatched incoming records are appended (inserted) to the target table. This mode is a good starting point when you want to keep your target table synchronized with the source data. Key fields must be defined to match the records.
Notes
- The target must already exist and should have an index defined to match the records.
- The types and sizes of the source fields chosen for the appending/updating must be compatible with existing target fields.
- Use this mode carefully when the key fields (either source or target) can contain NULL values.
- Use this mode carefully for multi-table exporting.
- This mode may work differently for different target database types/interfaces, therefore it is recommended to test it carefully before using on production systems. Consider to use different combinations of Memory saving mode and Use SQL parameters options to find the best results.
DELETE
The records in the target table that match incoming records, are deleted. Key fields must be defined to match the records.
Notes
- The target must already exist and should have an index defined to match the records.
- Use this mode carefully when the key fields (either source or target) can contain NULL values.
- Use this mode carefully for multi-table exporting.
- This mode may work differently for different target database types/interfaces, therefore it is recommended to test it carefully before using on production systems. Consider to use different combinations of Memory saving mode and Use SQL parameters options to find the best results.
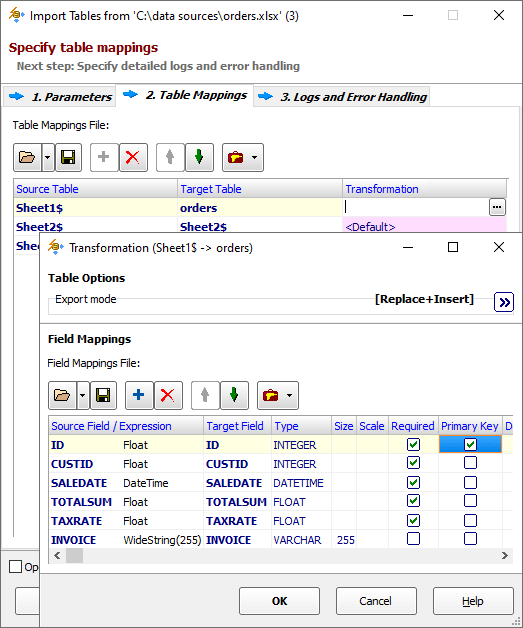
Using Export Mode in Multi-Table Exporting
When exporting or importing multiple datasets, you can specify the common export mode common for all datasets. But this value can be overridden later for each individual dataset-to-table pair in Table Mappings section when editing Transformation subsection for chosen pair:
Using Export Mode in Command Line
In the command line or action files, use the /ExportMode parameter to specify the export mode. For example:
- /ExportMode=APPEND
- /ExportMode=EMPTY+INSERT
See also