Here you can find the detailed instruction on how to export data from SQLite database to Microsoft Access database in Exportizer software.
Below, it is shown how to export data from GUI or command line.
Export Conditions
In most cases, to export from SQLite to Microsoft Access, the following conditions are required:
- SQLite3.dll must be accessible.
- Exportizer Pro or Exportizer Enterprise must be used.
- When using Exportizer Pro, the source and target databases must be connected via ODBC (using ADO interface), so make sure both SQLite ODBC driver and Microsoft Access ODBC driver were installed and the corresponding ODBC data sources were created. The drivers must be both either 32-bit or 64-bit.
- When using Exportizer Enterprise, the source SQLite database can be connected using FD interface, and SQLite ODBC driver is not required. If target Access database is an .mdb file, it can be connected via FD interface too; if it is an .accdb file, it can be connected either via ODBC driver or by using ADO interface and connection string specified.
- All involved components, i.e. Exportizer, ODBC drivers (if you use ODBC on source or target side), OLE DB providers (e.g. for Access .accdb file), should have the same architecture: 32-bit or 64-bit.
Notes
- If your operating system is 64-bit, you can install both 32-bit and 64-bit versions of the Exportizer software and use them independently.
- You can invoke the ODBC Data Source Administrator directly from Exportizer (in Open Data Source dialog) when it was launched in administrator mode.
SQLite to Access Exporting Preparation
If you are exporting data via GUI:
- Launch Exportizer Pro or Exportizer Enterprise.
- Register your source SQLite database:
- In Exportizer Pro, use ADO interface. The database must be an ODBC DSN, pointed to your SQLite database file.
- In Exportizer Enterprise, use FD interface. In most cases, specifying a pointer to the SQLite file is enough. Sometimes, specifying the Vendor library parameter may be needed: this must be a main DLL from the folder where SQLite installed, e.g. sqlite3.dll.
- Register your target MS Access database. Use ADO interface. If your target database file is .mdb (not .accdb), the FD interface could be used. In case of problems, try to play with different interfaces (ADO vs FD) or (better) build your own connection string for your Access database (ADO interface only) using examples from Exportizer documentation or from the Internet.
If the target database does not exist yet, create an .mdb or .accdb file. Exportizer Enterprise can create .mdb files. If you use Exportizer Pro or need to create an .accdb file, try MS Access or another application which is able to do that.
Note: You can register the target database from the Export dialog during the exporting.
Export Steps (GUI)
- Open the registered SQLite database or just drug and drop the source SQLite file onto the Exportizer table list.
- Choose a dataset or datasets to export:
- select a table from the table list;
or - open an SQL window, then write and execute an SQL query;
or - select multiple tables in the table list; before doing that, click Select Tables button
 ;
;
or - prepare a mix of multiple tables and/or SQL queries: open multiple tables one by one and multiple SQL windows; in SQL windows, write your database queries and execute them to get the result sets.
Please note that exporting multiple datasets at a time is available in Exportizer Enterprise only.
- select a table from the table list;
- Click Export button
 or choose a needed item from Export menu.
or choose a needed item from Export menu. - Switch to the Database tab. Select your registered Access database as a target database and set out specific export options. Some important notes:
- Turn on the Memory saving mode option and its related options. In case of exporting problems, if you suspect that they can be caused by these options, try different combinations of them.
- Choose the Export mode. To learn about all possible modes, read detailed description for Database export format. For multi-table exporting, this mode will be applied to the most of the tables, and you can override it for specific tables at the next step. For example, it can be Replace+Insert for the most of tables, and Update or Append for others etc.
- Leave the Table name field empty; otherwise, the data will be exported to one destination table.
- The bigger Commit interval value, the faster your exporting process. But too big value may cause memory and other issues. Therefore, try to play with it to find the optimal value before porting the solution to your production environment.
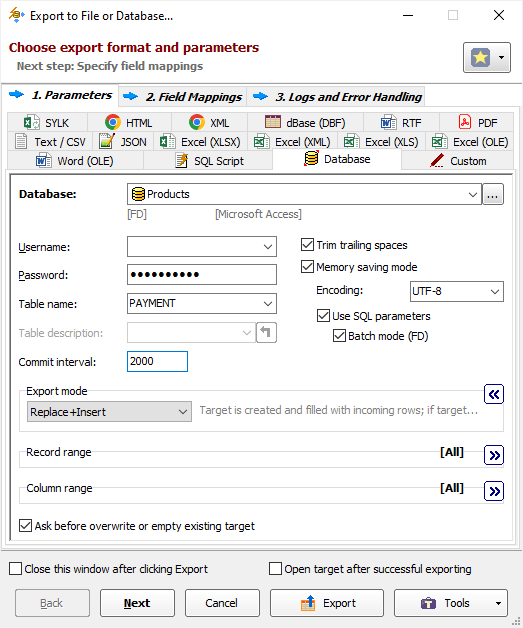
- Click Next. Specify the source-to-target mappings.
When you are exporting one dataset, you set the correspondence between the source and target fields/columns and specify target columns attributes.
For multi-table exporting, you specify the correspondence between the source datasets and target tables with optional editing nested field mappings and some other options like export mode.
- Click Export.
Exporting SQLite to Access from Command Line
SQLite to Access Command Line Examples
Exporting a SQLite table to existing Access database:
"C:\Program Files (x86)\Vitaliy Levchenko\Exportizer Enterprise 10\exptizer.exe" /export /ExportType=DATABASE /ExportMode=REPLACE+INSERT /IncludeMemo /MemorySaving /UseSQLParameters /UseBatchMode /Encoding=UTF-8 /SrcDBInterface=fd /SrcDBKind=FILE /SrcDBDriver=SQLITE "/SrcDB=C:\data sources\MyData\project.db" /SrcTableName=payments /TrgDBInterface=fd /TrgDBKind=FILE /TrgDBDriver=Access "/TrgDB=C:\data sources\MyData\Products.mdb" /TrgTableName=PAYMENTThe same as above, but in silent mode and using a log file:
"C:\Program Files (x86)\Vitaliy Levchenko\Exportizer Enterprise 10\exptizer.exe" /silent /export /ExportType=DATABASE /ExportMode=REPLACE+INSERT /IncludeMemo /MemorySaving /UseSQLParameters /UseBatchMode /Encoding=UTF-8 /SrcDBInterface=fd /SrcDBKind=FILE /SrcDBDriver=SQLITE "/SrcDB=C:\data sources\MyData\project.db" /SrcTableName=payments /TrgDBInterface=fd /TrgDBKind=FILE /TrgDBDriver=Access "/TrgDB=C:\data sources\MyData\Products.mdb" /TrgTableName=PAYMENT /LogFile=C:\Test\export.logExporting all tables from SQLite database to existing Access database in silent mode:
"C:\Program Files (x86)\Vitaliy Levchenko\Exportizer Enterprise 10\exptizer.exe" /silent /export /ExportType=DATABASE /ExportMode=REPLACE+INSERT /IncludeMemo /MemorySaving /UseSQLParameters /UseBatchMode /Encoding=UTF-8 /SrcDBInterface=fd /SrcDBKind=FILE /SrcDBDriver=SQLITE "/SrcDB=C:\data sources\MyData\project.db" /SrcTableName=* /TrgDBInterface=fd /TrgDBKind=FILE /TrgDBDriver=Access "/TrgDB=C:\data sources\MyData\Products.mdb" /TrgTableName=* /LogFile=C:\Test\export.logThe same as above, but creating Access database on the fly (if does not exist):
"C:\Program Files (x86)\Vitaliy Levchenko\Exportizer Enterprise 10\exptizer.exe" /silent /export /ExportType=DATABASE /ExportMode=REPLACE+INSERT /IncludeMemo /MemorySaving /UseSQLParameters /UseBatchMode /Encoding=UTF-8 /SrcDBInterface=fd /SrcDBKind=FILE /SrcDBDriver=SQLITE "/SrcDB=C:\data sources\MyData\project.db" /SrcTableName=* /TrgDBInterface=fd /TrgDBKind=FILE /TrgDBDriver=Access "/TrgDB=C:\data sources\MyData\Products.mdb" /TrgTableName=* /LogFile=C:\Test\export.log /CreateTargetContainerNote: You can add other parameters to the command lines above according to the command line specification.
SQLite to Access Action File Example
The last command line above can be transformed to an action file, which is much more comfortable to work with. You can run action files either form the command line or from Exportizer GUI. The action file contains all the command line parameters (except /silent switch), one parameter per line, and allows comments:
/export
/ExportType=DATABASE
/ExportMode=REPLACE+INSERT
/IncludeMemo
/MemorySaving
/UseSQLParameters
/UseBatchMode
/Encoding=UTF-8
/SrcDBInterface=fd
/SrcDBKind=FILE
/SrcDBDriver=SQLite
/SrcDB=C:\data sources\MyData\project.db
/SrcTableName=* ;Export all tables from SQLite database
/TrgDBInterface=fd
/TrgDBKind=FILE
/TrgDBDriver=Access
/TrgDB=C:\data sources\MyData\Products.mdb
/TrgTableName=*
/LogFile=C:\Test\export.log
/CreateTargetContainerIf you save the file, for example, as C:\Export\SQLite2Access.txt, then your command line will look like:
"C:\Program Files (x86)\Vitaliy Levchenko\Exportizer Enterprise 10\exptizer.exe" /silent /ActionFile=C:\Export\SQLite2Access.txtAlternative Scenario Using SQL
If you have reasons not to export data to Access database directly, you can export the SQLite data in Exportizer to a SQL script first, and then load data from the script in Exportizer or using an external SQL tool. And, of course, you can export data to SQL script either by GUI or from the command line.
But please note, that when choosing exporting via SQL script, your export process will have two phases: first, exporting the data to SQL script; second, loading data from the script to your target database. So, this way can be less effective, especially for large datasets or when automating the data exporting. Another disadvantage of this way is that BLOB data will not be transferred.
Anyway, you can try both export scenarios and select the fastest and/or the most convenient one.
See also